“`html
Understanding the Differences Between Hardwood and Softwood
In the world of carpentry and forestry, wood is often categorized into two primary types: hardwood and softwood. While the names may imply otherwise, the classification is not necessarily based on the hardness of the wood. This comprehensive guide will explore the key differences between hardwood and softwood, covering aspects such as their sources, physical traits, strength, cost, and applications. By the end of this article, you’ll have a better understanding of which type of wood might be best for your needs.
Softwood vs Hardwood
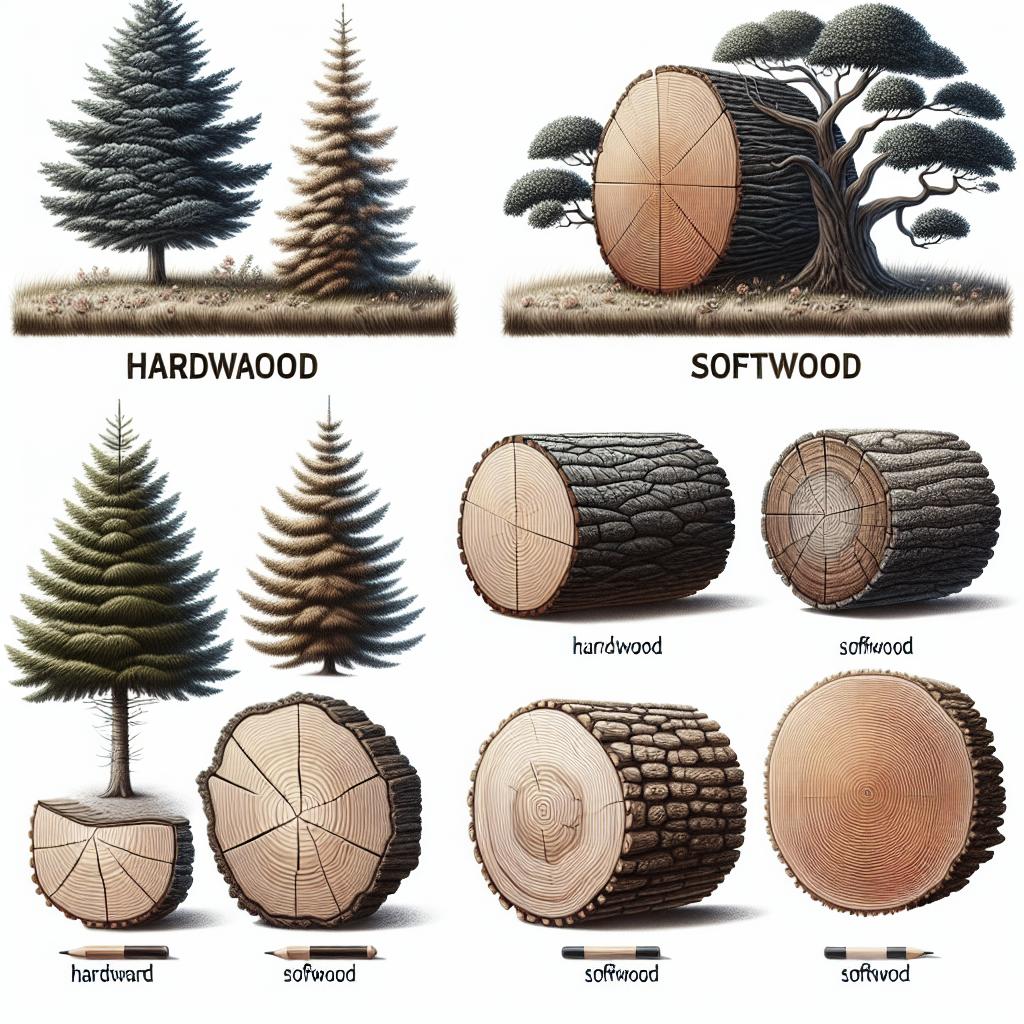
Softwood and hardwood have fundamental differences that go beyond their names. While softwood is often thought to be softer than hardwood, this is not always the case. The terms pertain to the botanical origin of the wood rather than its physical characteristics.
Softwood comes from coniferous trees, whereas hardwood is harvested from deciduous trees. The main distinction is in the tree reproduction process: softwoods have seeds without coverings, unlike hardwoods whose seeds have a protective layer.
What is the Difference Between Hardwood and Softwood Lumber?
The major difference lies in their respective cell structures. Softwood generally has a simpler structure, which contributes to its commonly lighter weight. This structural difference is also why softwoods are more abundant and quicker to grow compared to hardwoods.
Hardwood lumber tends to be denser due to its complex cell structure. This makes it ideal for high-quality furniture, flooring, and detailed woodwork where durability and strength are paramount.
What Types of Trees do Hardwood and Softwood Come From?
Softwood trees, primarily evergreens like pine, fir, cedar, and spruce, are more abundant globally. They tend to grow faster and are commonly used for construction purposes due to their easy availability.
Hardwood trees such as oak, maple, birch, and walnut lose their leaves annually. These trees typically take longer to mature, which adds to their cost but also makes them less environmentally intrusive, as they are often sustainably managed.
Strength and Durability
Generally, hardwood is considered to be stronger and more durable than softwood. This intrinsic strength makes hardwood the preferred choice for applications where longevity is crucial, such as in construction and furniture making.
Softwoods, while less durable, are easier to work with due to their lighter weight and lower density. This versatility makes them ideal for producing paper, packaging, and many construction projects where flexibility is more beneficial than raw strength.
Density and Hardness
Hardwood’s high density contributes to its hardness and toughness, making it an ideal candidate for fine woodworking projects. Its density enables it to withstand significant wear and tear, which is a desirable quality for furniture and flooring.
Softwood, in contrast, has a lower density and is typically softer, which allows for easier manipulation when constructing frameworks or decorative objects. The relative softness of softwood facilitates faster and simpler processing.
Physical Characteristics and Appearance
Knots and Character
Softwoods typically have more knots compared to hardwoods, which can add character and a rustic appearance when used in visible structures. However, too many knots can compromise the structural integrity of the wood.
Color
The color of wood can significantly influence its application. Hardwood features a variety of rich tones and grains, ranging from deep reds to chocolate browns. These hues make it highly desirable for aesthetic applications.
Softwoods tend to be lighter in color, with variations of white to pale yellow. This lighter color palette can be beneficial when a project requires painting or staining, offering a neutral base.
How to Tell Hardwood and Softwood Apart
One can often distinguish between hardwood and softwood by examining the grain and color. Hardwood generally has a more intricate and pronounced grain pattern, whereas softwood’s grain is typically straight and less distinct.
The presence of resin is another noticeable difference; softwoods often contain resins, giving them a distinctive smell, while hardwoods usually do not. Additionally, the weight test can be a quick method, with hardwoods generally being heavier due to their density.
Cost and Availability
Softwood is generally cheaper and more widely available than hardwood due to the faster growth of coniferous trees. Its affordability makes it a common choice for many construction and industry applications.
Hardwood, on the other hand, is more expensive mainly due to the longer growth period and greater labor effort required for production. Consequently, it is used primarily in projects where aesthetics and durability justify the higher price.
Common Uses of Softwood vs. Hardwood
What is Softwood Used For?
Softwood is extensively used in construction, specifically for framing houses, roofs, and in the form of plywood. Its characteristics make it optimal for mass production and applications requiring ease of shaping and cutting.
Besides construction, softwood is also a preferred material for making pulp, which is then processed into paper and other packaging materials.
What is Hardwood Used For?
Hardwood finds its primary applications in high-quality furniture, flooring, and cabinetry. The beauty and durability of hardwood make it an exceptional choice for any project that demands high aesthetic value.
Additionally, hardwood is frequently used in the production of items like musical instruments and sports equipment, where durability under repeated use is crucial.
Summary of Main Points
Frequently Answered Questions
| Aspect | Softwood | Hardwood |
|---|---|---|
| Source Trees | Coniferous Trees | Deciduous Trees |
| Growth Rate | Fast | Slow |
| Density | Lower Density | Higher Density |
| Color | Lighter Colors | Darker Rich Tones |
| Cost | More Affordable | More Expensive |
| Common Use | Construction, Paper | Furniture, Flooring |
About the Author
Lucas Martin is a journalism and communications graduate with a passion for engaging writing. With expertise in research and grammar, Lucas is keenly interested in topics related to technology and innovation. Eager to expand his skills in SEO writing, Lucas dedicatedly stays on top of market trends.
“`